중력작용 (프로그래머스 Lv5)
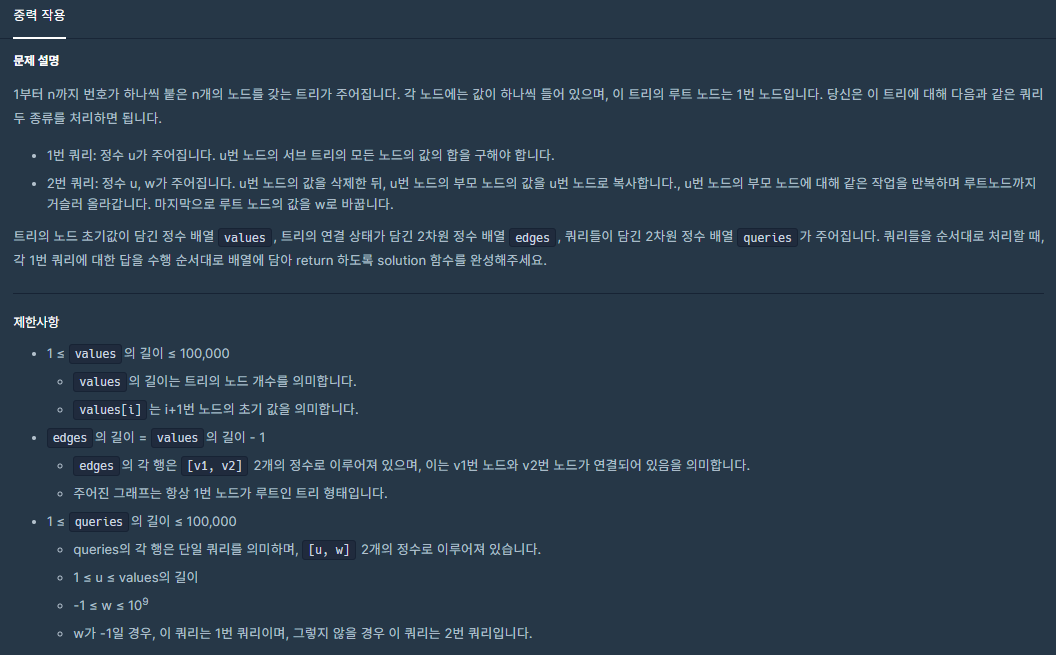
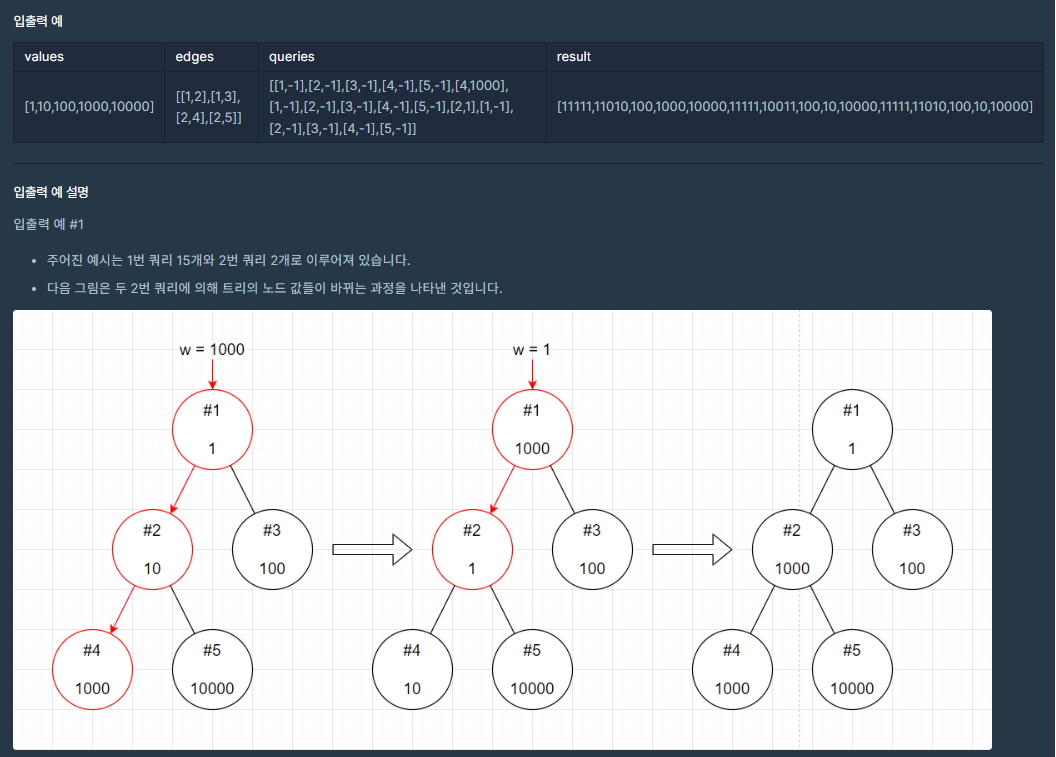
코드의 작동원리 설명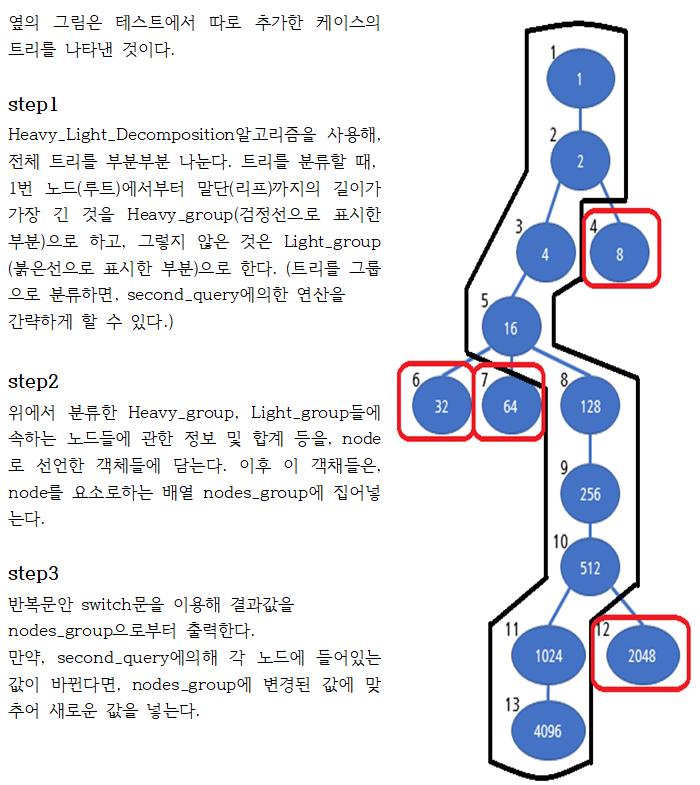
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
node[] nodes_group;
public ArrayList<Long> solution(int[] values, int[][] edges, int[][] queries)
{
long[] answer;
ArrayList<Long> result = new ArrayList<Long>();
int len = values.length;
nodes_group = new node[len];
//아래처럼 해줘야한다.
//node를 요소로 가지는 배열을 위에서 선언만 했을 뿐,
//실제 초기화된 노드가 들어가 있는것은 아니다.
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{
nodes_group[i] = new node();
nodes_group[i].val = values[i];
}
//edges의 크기가 클 경우, for문안에 조건식을 넣어, node_connec관련 코딩을
//한다면 시간이 많이 소요된다.
for(int j=0; j<edges.length; j++)
{
nodes_group[edges[j][0]-1].node_connec.add(edges[j][1]);
nodes_group[edges[j][1]-1].node_connec.add(edges[j][0]);
}
/* 위의 반복문 실행 후, nodes_group출력
[
{"total":0,"val":1,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[2,3]},
{"total":0,"val":10,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[1,4,5]},
{"total":0,"val":100,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[1]},
{"total":0,"val":1000,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[2]},
{"total":0,"val":10000,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[2]}
]
*/
seperation(1,0);
/*seperation실행 후, nodes_group출력
[
{"total":11111,"val":1,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"vals":[1,10,1000],"idxs":[1,2,4],"sub_totals":[11110,11000,0],"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[2,3]},
{"total":11010,"val":10,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"vals":[1,10,1000],"idxs":[1,2,4],"sub_totals":[11110,11000,0],"loc_in_group":1,"node_connec":[4,5]},
{"total":100,"val":100,"connected_node_to_upper_group":1,"vals":[100],"idxs":[3],"sub_totals":[0],"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[]},
{"total":1000,"val":1000,"connected_node_to_upper_group":0,"vals":[1,10,1000],"idxs":[1,2,4],"sub_totals":[11110,11000,0],"loc_in_group":2,"node_connec":[]},
{"total":10000,"val":10000,"connected_node_to_upper_group":2,"vals":[10000],"idxs":[5],"sub_totals":[0],"loc_in_group":0,"node_connec":[]}
]
*/
int where_is=-1;
for(int[] query: queries)
{
switch(query[1])
{
case -1:
where_is = nodes_group[query[0]-1].loc_in_group;
result.add(nodes_group[query[0]-1].vals[where_is]+nodes_group[query[0]-1].sub_totals[where_is]);
break;
default:
second_query(query[0],query[1]);
break;
}
}
return result;
}
//node[] nodes_group;을 메소드의 인수로 넣지 않고도, 함수의 연산과정에서 사용하기 위해
//함수 선언시 static으로 선언하면 안된다.(정적 메소드로 선언하면 안된다.)
// 1번 노드 2번 노드 3번 노드 4번 노드 5번 노드
//["node_connec":[2,3]},"node_connec":[1,4,5]},"node_connec":[1]},"node_connec":[2]},"node_connec":[2]}]
//node_connec에서의 정보를 활용해 노드들을 그룹화 해서 나눈다.(Heavy_Light_Decomposition알고리즘 사용)
ArrayList<Integer> seperation(int node_num, int ances)
{
int reit_node_num = node_num;
boolean root_node = (node_num==1) ? true : false;
ArrayList<Integer> indexs = new ArrayList<Integer>();
indexs.add(reit_node_num);
ArrayList<Integer> temp_c = nodes_group[node_num-1].node_connec;
//node_connec에는 현제의 노드를 중심으로 위,아래로 연결된 노드의 번호가 들어가 있다.
//아래 if문을 통해 node_connec에서 위로 연결된 노드의 번호를 제거한다.
if(ances > 0)
{
temp_c.remove(Integer.valueOf(ances));
}
//node_connec에서 위로 연결된 노드의 번호를 제거한 후, 아래로 연결된 노드 번호가 하나만
//남아있다면, 불필요한 재귀함수의 호출을 줄여주기위해, 아래와 같이 while문을 사용해서 처리한다.
//(while문 다음에 있는 조건문 if(temp_c.size() >=2)에서 재귀함수 사용하는데, 재귀가 깊어지면
//stackoverflow가 발생하는 경우가 있다. 재귀함수 사용을 줄이면 속도 향상에도 도움이 된다.)
while(temp_c.size()==1)
{
ances = reit_node_num;
reit_node_num = temp_c.get(0);
temp_c = nodes_group[reit_node_num-1].node_connec;
temp_c.remove(Integer.valueOf(ances));
indexs.add(reit_node_num);
}
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> indexs_g = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> contain;
//위의 while문을 탈출하였다면, 현재의 노드(=temp_c)아래로 연결된 가지가 2개 이상인 지점에
//도달했다는 것을 의미한다.
if(temp_c.size() >=2)
{
int max_len = 0;
boolean max = false;
for(int idx : temp_c)
{
//temp_c아래로 뻗은 가지들이 각각 leaf까지 도달했을 때의 경로를 seperation 함수가
//ArrayList<Integer>의 형태로 반환하고, 그 값을 contain에 저장한다.
contain = seperation(idx,reit_node_num);
if(contain.size() > max_len)
{
max_len = contain.size();
}
//temp_c아래로 뻗은 가지들이 각각 leaf까지 도달했을 때의 경로를 indexs_g에 요소로 넣는다.
indexs_g.add(contain);
}
for(ArrayList<Integer> idx_s: indexs_g)
{
//temp_c아래로 뻗은 가지들 중 가장 긴 경로를 가진 경우
if(!max && idx_s.size() == max_len)
{
//가장 긴 경로를 indexs에 추가한다.
//(heavy_group축출하는 과정,indexs에 들어있는 배열이 최종적으로 heavy_group인것은
//아직 확인된건 아니다.)
indexs.addAll(idx_s);
max = true;
}
else
{
//temp_c아래로 뻗은 가지들 중 가장 긴 경로를 제외한 나머지 경로들
//sub_que_sum메소드의 인수로 넣어 함수를 실행한다.
//(light_group들을 축출)
sub_que_sum(idx_s,reit_node_num);
}
}
}
if(root_node)
{
//최종적으로 구한 heavy_group(=indexs)을 sub_que_sum메소드의 인수로
//집어넣는다.
sub_que_sum(indexs,0);
return indexs;
}
else
{
return indexs;
}
}
//seperation메소드에서 나눈 그룹들(=idx_s,indexs)에 대한 연산을 sub_que_sum에서 진행한다.
void sub_que_sum(ArrayList<Integer> indexs, int reit_node_num)
{
int[] vals = new int[indexs.size()];
int[] idxs = new int[indexs.size()];
long[] sub_totals = new long[indexs.size()];
int idx = indexs.size()-1;
while(idx>-1)
{
long sub_sums = 0;
//indexs의 맨뒤의 값들부터 차례로 cur_sub_node_num에 넣는 과정을 while문을 통해 진행한다.
int cur_sub_node_num = indexs.get(idx);
ArrayList<Integer> sub_node_connec = nodes_group[cur_sub_node_num-1].node_connec;
//cur_sub_node_num의 번호를 가진 노드에, 본래의 가지(indexs)외의 다른 그룹들(light_group)과 연결된
//가지가 있는지 확인한다.
if(sub_node_connec.size() >0)
{
//다른 light_group 그룹들의 합계(=nodes_group[sub_num-1].total)를 sub_sums에 더해준다.
for(int sub_num : sub_node_connec)
{
sub_sums += nodes_group[sub_num-1].total;
}
}
//현재의 노드의 값(=val)에 sub_sums을 더한것을 total에 저장한다.
nodes_group[cur_sub_node_num-1].total = nodes_group[cur_sub_node_num-1].val+sub_sums;
//ArrayList<Integer> indexs에서 cur_sub_node_num의 위치한 좌표를 loc_in_group에 저장한다.
nodes_group[cur_sub_node_num-1].loc_in_group = idx;
//위에서 구한 val,cur_sub_node_num,sub_sums에 관한 정보를 배열에 저장한다.
vals[idx] = nodes_group[cur_sub_node_num-1].val;
idxs[idx] = cur_sub_node_num;
sub_totals[idx] = sub_sums;
idx -=1;
}
//위의 반복문에 결과 vals,idxs,sub_totals에는 값들이 채위지게된다.
//vals,idxs,sub_totals,reit_node_num을 indexs에 들어있는 번호에 해당하는 노드에
//집어넣어준다.(배열이 얕은 복사가되게 해서, 나중에 second_query에의해 특정
//노드에서 vals,idxs,sub_totals의 값들이 바뀌면, 해당노드가 속한 그룹의 나머지 노드에서도
//동일하게 vals,idxs,sub_totals의 값들이 변경되게 하려는 의도다.)
for(int id : indexs)
{
nodes_group[id-1].connected_node_to_upper_group = reit_node_num;
nodes_group[id-1].vals = vals;
nodes_group[id-1].idxs = idxs;
nodes_group[id-1].sub_totals = sub_totals;
}
}
void second_query(int idx, int val)
{
int upper;
int upper_loc_value=0;
int present_idx = idx;
//second_query실행의 결과 삭제될 값을 value_to_be_deleted에 저장한다.
int value_to_be_deleted=nodes_group[present_idx-1].vals[nodes_group[present_idx-1].loc_in_group];
do
{
//현재 노드는 그것이 속한 그룹 위에 상위 그룹의 특정노드와 연결되어 있다.
//상위 그룹의 특정노드의 번호를 upper에 저장한다.
upper = nodes_group[present_idx-1].connected_node_to_upper_group;
//second_query실행의 결과 기존의 노드에 있던 값을 밀어내고 새로 들어올 값을 upper_loc_value에 저장한다.
//(upper가 0이면, present_idx가 1이고, 이것은 최상위 rootnode를 의미하므로, upper_loc_value값은 val가
//된다.
//만약 0이 아니라면, upper_loc_value값은 현재 노드의 값을 집어넣어야 한다.)
upper_loc_value = (upper!=0) ? nodes_group[upper-1].vals[nodes_group[upper-1].loc_in_group]
: val;
//현재 노드가 속한 그룹이 하나 이상의 노드로 묶여있는지 확인한다.
if(nodes_group[present_idx-1].vals.length > 1)
{
//그룹에 속한 각각의 노드의 sub_totals에, second_query실행으로 인한
//sub_totals값의 변화치를 더해준다.
for(int j=0; j<=nodes_group[present_idx-1].loc_in_group; j++)
{
nodes_group[present_idx-1].sub_totals[j] += nodes_group[present_idx-1].vals[j] - value_to_be_deleted;
}
//second_query실행결과 vals의 변화또한 반영해 준다.
/*System.arraycopy를 사용하면 sublist등을 사용해 배열의 값을 바꿀필요 없이 쉽게 변경이 가능하다.
System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
src - 원본 배열
srcPos - 원본 배열의 복사 시작 위치
dest - 복사할 배열
destPost - 복사할 배열의 복사 시작 위치
length - 복사할 요소의 개수
*/
System.arraycopy(nodes_group[present_idx-1].vals,0,nodes_group[present_idx-1].vals,1,nodes_group[present_idx-1].loc_in_group);
}
nodes_group[present_idx-1].vals[0] = upper_loc_value;
present_idx = upper;
}
while(upper !=0);
}
}
class node
{
long total=0;
int val;
int connected_node_to_upper_group;
int[] vals;
int[] idxs;
long[] sub_totals;
int loc_in_group;
ArrayList<Integer> node_connec = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
실행결과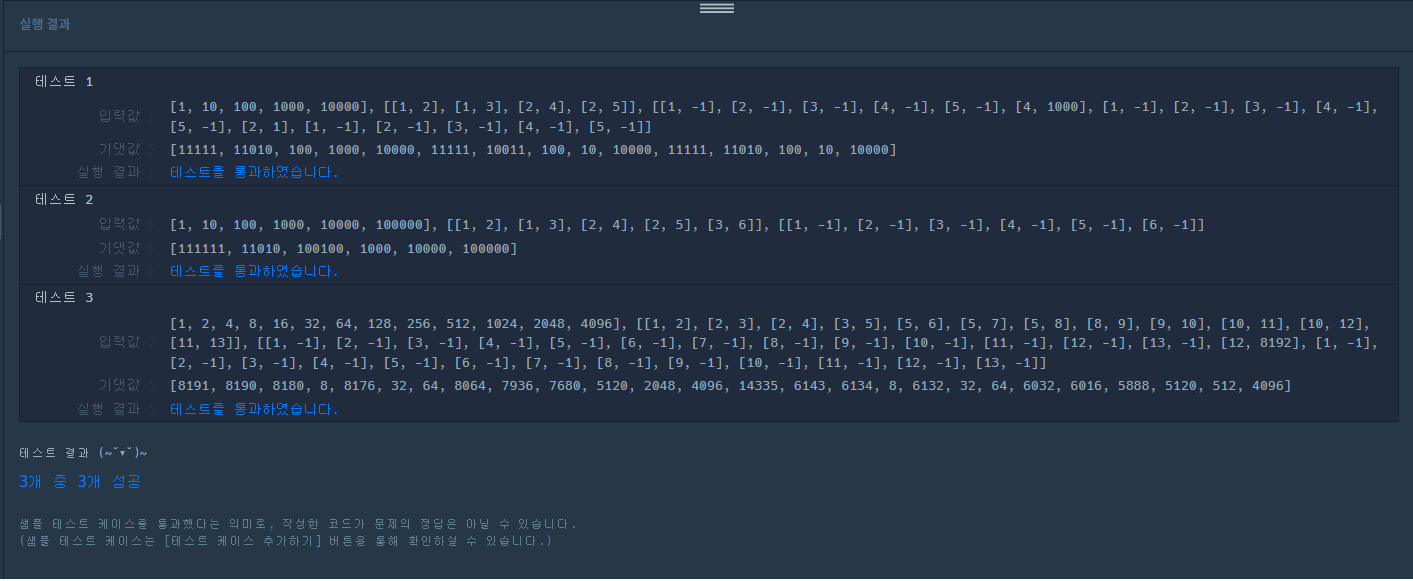
댓글남기기