지형이동(프로그래머스 Lv4)

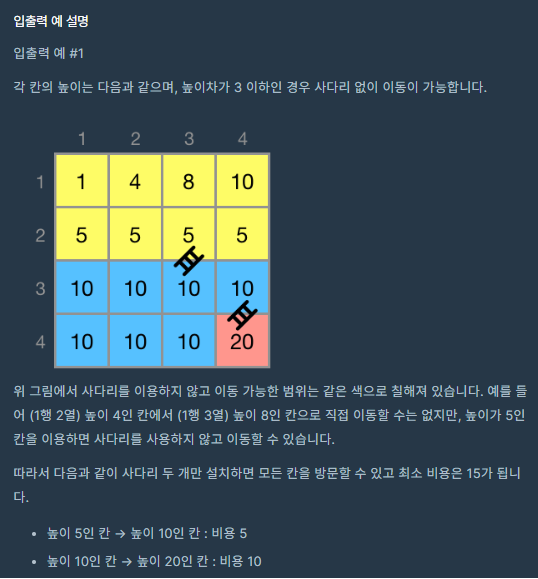
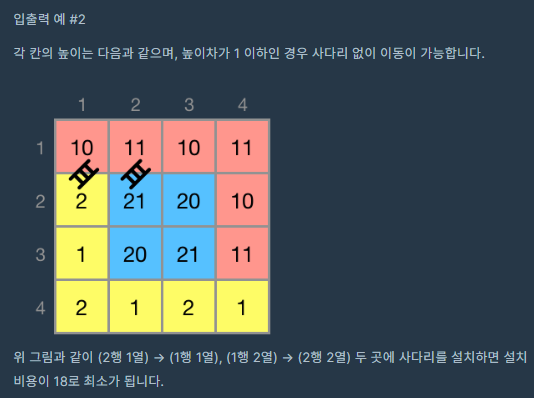
코드의 작동원리 설명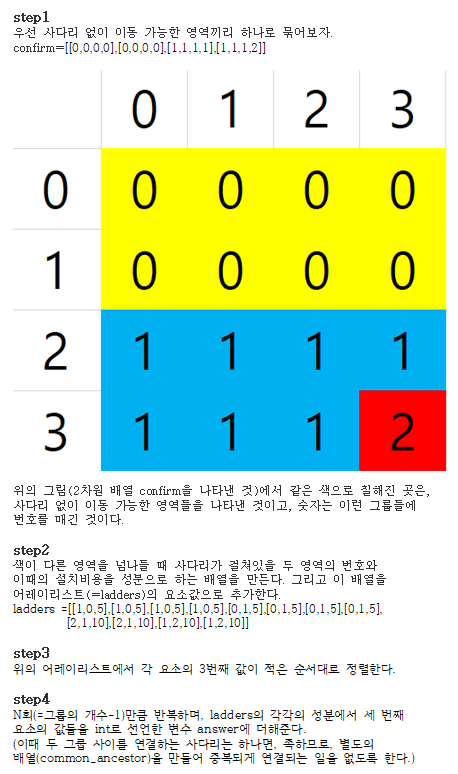
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
public static int[] common_ancestor;
public static int[][] confirm;
public int solution(int[][] land, int height)
{
int answer = 0;
int num = land.length;
confirm = new int[num][num];
//num x num 배열의 값을 모드 -1로 초기화 시킨다.
for(int i=0; i<num; i++)
{
//Arrays.fill(confirm[i], -1);
for(int j=0; j<num; j++)
{
confirm[i][j] = -1;
}
}
// w,e,n,s = (-1,1,-1,1)
ArrayList<Integer> incre = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(-1,1,-1,1));
Queue<ArrayList<Integer>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int region = 0;
for(int i=0; i<num; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<num; j++)
{
//confirm[i][j]의 값이 -1(초기화 했던 값)이 아닌경우
//(사다리 없이 갈수 있는 곳으로 묶인경우)
if(confirm[i][j] > -1)
{
continue;
}
//confirm[i][j]의 값이 -1(초기화 했던 값)인 경우
else
{
queue.offer(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(i,j)));
confirm[i][j] = region;
//connec의 실행결과 confirm[i][j]에 구역번호(region)가 할당된다.
//그리고 할당된 구역번호에 +1을한 값이 반환되어 region에 들어간다.(region = region +1)
region = connec(land,height,incre,queue,confirm, region);
}
}
}
//여기까지 실행결과(of confirm)
/*
[
[0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,2]
]
*/
//공통영역의 갯수의 크기를 가지는 배열(=common_ancestor) 선언하고
//0,1,2,...,num값으로 초기화 시킨다.
common_ancestor = new int[region+1];
int n = 0;
while(n < region+1)
{
common_ancestor[n] = n;
n +=1;
}
//common_ancestor==[0,1,2]
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ladders = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i=0; i<num; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<num; j++)
{
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int pos = k/2;
int aug = incre.get(k);
int len = land.length;
// w,e, n,s
//-1,1,-1,1
/*k에 따른 i,j값 설정
k=0 => (i,j) = (i-1,j)
k=1 => (i,j) = (i+1,j)
k=2 => (i,j) = (i,j-1)
k=3 => (i,j) = (i,j+1)
*/
int new_i = (pos == 1) ? i+aug : i;
int new_j = (pos == 0) ? j+aug : j;
//n x n구역 벗어날 시
if(new_i < 0 || new_i>=len || new_j < 0 || new_j>=len)
{
continue;
}
//이동한 곳이 이미 같은 영역인 경우
if(confirm[new_i][new_j] == confirm[i][j])
{
continue;
}
//이동한 곳이 다른 영역(=사다리 없이 못가는 영역)인 경우
int height_comp = Math.abs(land[new_i][new_j]-land[i][j]);
ladders.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(confirm[new_i][new_j],
confirm[i][j],height_comp)));
}
}
}
//여기까지 실행한결과(of ladders)
//[[1,0,5],[1,0,5],[1,0,5],[1,0,5],[0,1,5],[0,1,5],
//[0,1,5],[0,1,5],[2,1,10],[2,1,10],[1,2,10],[1,2,10]]
//ladders배열의 원소를, 각 원소의 마지막 요소인 height_comp가 작은순으로 정렬하기 위한 작업
//Comparator학습하자.
//참고 : https://www.daleseo.com/java-comparable-comparator/
Comparator<ArrayList<Integer>> comparator = new Comparator<ArrayList<Integer>>()
{
@Override
public int compare(ArrayList<Integer> first, ArrayList<Integer> second)
{
int res = first.get(2) - second.get(2);
int res2 = first.get(1) - second.get(1);
//height_comp가 작은 순으로 정렬
//만약 first, second의 height_comp가 같다면, first.get(1)과 second.get(1)을
//작은 순으로 정렬한다.
//음수 => 앞에거 먼저 정렬, 양수=>앞뒤 순서 바꿈
//(반드시 -1, 1일 필요는 없다, 걍 음수 양수 구분만 하기 위한 용도일 뿐이다.)
return res = (res < 0) ? -1 : (res > 0 ? 1 : (res2 < 0 ? -1 : 1));
}
};
//위의 과정을 생략하고 싶다면 아래와 같이 해도 무관한다.
//Collections.sort(players, (first, second) -> first.getScore() - second.getScore());
Collections.sort(ladders, comparator);
int number_of_ladder = 0;
for(ArrayList<Integer> ladder : ladders)
{
if(check_ances(ladder.get(0))!=check_ances(ladder.get(1)))
{
merge(ladder.get(0), ladder.get(1));
answer += ladder.get(2);
number_of_ladder +=1;
//총 사다리의 개수는 나뉘어진 영억의 개수보다 1개 적어야 한다.
if(number_of_ladder == region)
{
break;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
//너비우선탐색 알고리즘 이용
public static int connec(int[][] land, int height,
ArrayList<Integer> incre,
Queue<ArrayList<Integer>> queue,
int [][] confirm,
int region)
{
while(queue.size() !=0)
{
ArrayList<Integer> c = new ArrayList<Integer>();
c.addAll(queue.poll());
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int pos = k/2;
int aug = incre.get(k);
int len = land.length;
// w,e, n,s
/*k에 따른 i,j값 설정
k=0 => (i,j) = (i-1,j)
k=1 => (i,j) = (i+1,j)
k=2 => (i,j) = (i,j-1)
k=3 => (i,j) = (i,j+1)
*/
//-1,1,-1,1
int i = (pos == 1) ? c.get(0)+aug : c.get(0);
int j = (pos == 0) ? c.get(1)+aug : c.get(1);
//n x n구역 벗어날 시
if(i < 0 || i==len || j < 0 || j==len)
{
continue;
}
//이미 구역이 정해진 경우
if(confirm[i][j] > -1)
{
continue;
}
//사다리가 필요한 경우
if(Math.abs(land[i][j]-land[c.get(0)][c.get(1)]) > height)
{
continue;
}
confirm[i][j] = region;
queue.offer(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(i,j)));
}
}
return region +=1;
}
//공통인 구역의 탐색
public static int check_ances(int num)
{
if (num==common_ancestor[num])
{
//num가 현재 구역의 공통 구역일 때
return num;
}
//공통 구역이 아니라면, 재탐색(재귀함수 이용)
return common_ancestor[num] = check_ances(common_ancestor[num]);
}
//공통인 구역으로 묶기
public static void merge(int former , int latter)
{
//첫 번째 인자의 공통 구역 탐색
former = check_ances(former);
//두 번째 인자의 공통 구역 탐색
latter = check_ances(latter);
if (former < latter)
{
//두 구역중 작은쪽을 공통 구역으로 묶어준다.
common_ancestor[latter] = former;
}
//former >= latter
else
{
common_ancestor[former] = latter;
}
}
}
실행결과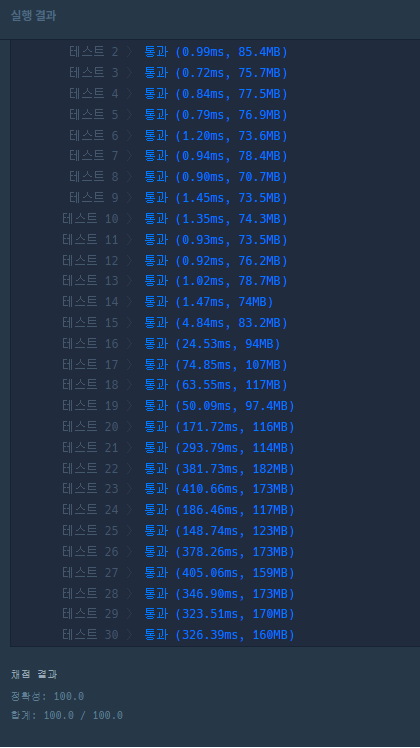
댓글남기기