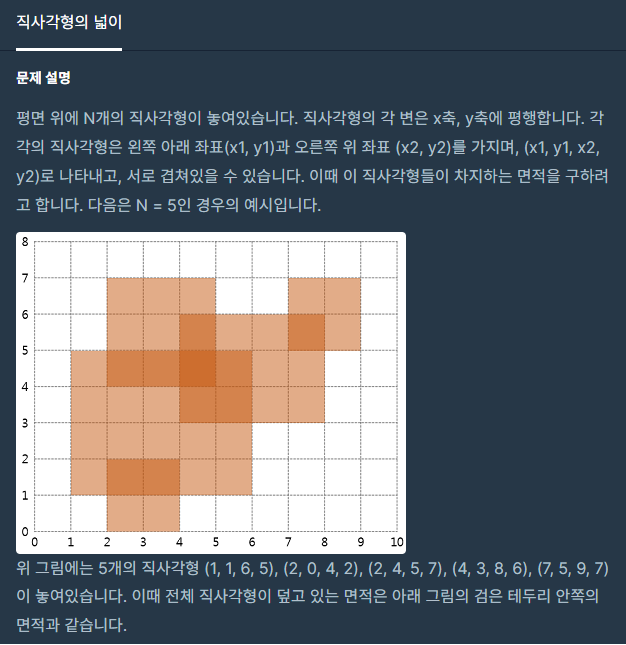
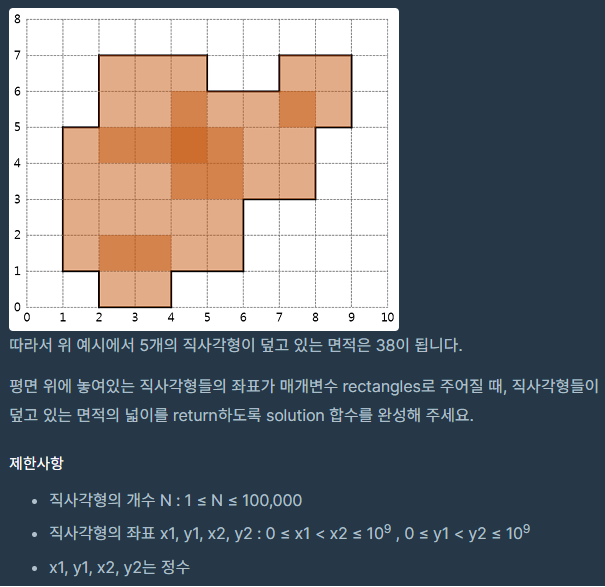
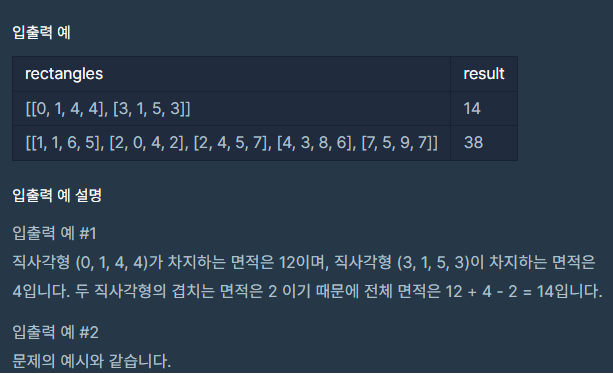
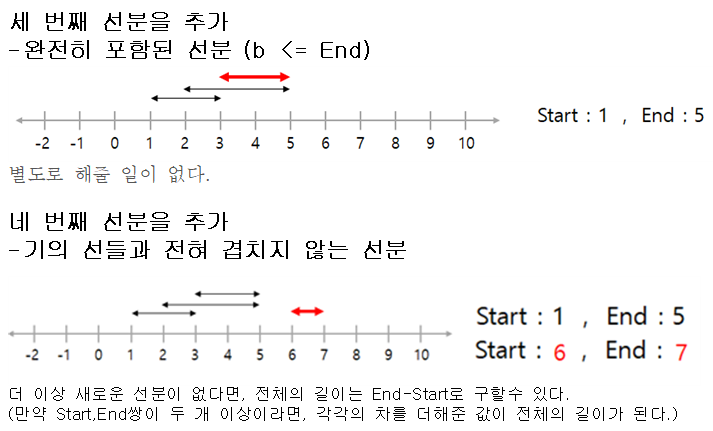
직사각형의 넓이1(프로그래머스 Lv5)
코드의 작동원리 설명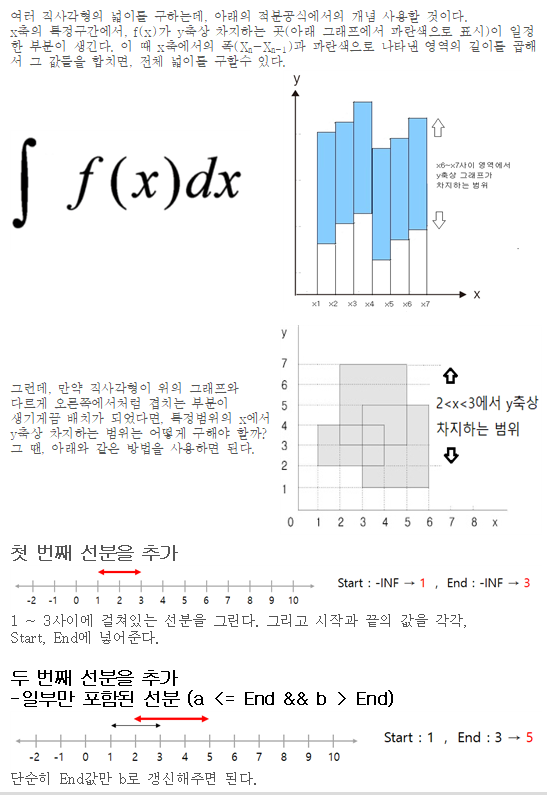
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
//HashMap<Integer, HashSet<vertical_length>>
public long solution(int[][] rectangles)
//public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> solution(int[][] rectangles)
{
HashSet<Integer> set_x = new HashSet<Integer>();
HashSet<Integer> set_y = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int[] rectangle : rectangles)
{
set_x.add(rectangle[0]);
set_x.add(rectangle[2]);
set_y.add(rectangle[1]);
set_y.add(rectangle[3]);
//rectangle[2]-rectangle[0] => x_diff
//rectangle[3]-rectangle[1] => y_diff
}
List<Integer> Set_x = new ArrayList(set_x);
List<Integer> Set_y = new ArrayList(set_y);
//오름차순으로 Set_x,Set_y을 정렬한다.
Collections.sort(Set_x);
Collections.sort(Set_y);
/*
Set_x
[0,3,4,5]
[1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Set_y
[1,3,4]
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
*/
for(int i=0;i<rectangles.length; i++)
{
rectangles[i][0]=Set_x.indexOf(rectangles[i][0]);
rectangles[i][2]=Set_x.indexOf(rectangles[i][2]);
rectangles[i][1]=Set_y.indexOf(rectangles[i][1]);
rectangles[i][3]=Set_y.indexOf(rectangles[i][3]);
}
/*
rectangles
[[0,0,2,2],[1,0,3,1]]
[[0,1,4,5],[1,0,2,2],[1,4,3,7],[2,3,6,6],[5,5,7,7]]
*/
int position_max=-1;
int position_min=-1;
vertical_length temp_vertical;
Iterator<vertical_length> iterator;
vertical_length current;
HashSet<vertical_length> verticals;
HashSet<vertical_length> removal;
HashMap<Integer, HashSet<vertical_length>> map = new HashMap<Integer, HashSet<vertical_length>>();
/*
rectangles
[[0,0,2,2],[1,0,3,1]]
[[0,1,4,5],[1,0,2,2],[1,4,3,7],[2,3,6,6],[5,5,7,7]]
*/
for(int[] rectangle : rectangles)
{
for(int i=rectangle[0]; i<rectangle[2]; i++)
{
temp_vertical = new vertical_length();
//temp_vertical.position = new int[]{rectangle[1],rectangle[3]};
temp_vertical.position[0] = rectangle[1];
temp_vertical.position[1] = rectangle[3];
if(!map.containsKey(i))
{
verticals = new HashSet<vertical_length>();
verticals.add(temp_vertical);
map.put(i, verticals);
}
/*
{
"0":[{"position":[1,5]}],
"1":[{"position":[0,2]},{"position":[4,7]},{"position":[1,5]}],
"2":[{"position":[4,7]},{"position":[3,6]},{"position":[1,5]}],
"3":[{"position":[3,6]},{"position":[1,5]}],
"4":[{"position":[3,6]}],
"5":[{"position":[5,7]},{"position":[3,6]}],
"6":[{"position":[5,7]}]
}
*/
else
{
//iterator = verticals.iterator();
iterator = map.get(i).iterator();
removal = new HashSet<vertical_length>();
while(iterator.hasNext())
{
current = iterator.next();
position_max = current.position[1];
position_min = current.position[0];
//temp_vertical의 max가 current의 min, max사이에 있을경우
if(position_min<= temp_vertical.position[1] && temp_vertical.position[1] <=position_max)
{
//temp_vertical의 min이 current의 min보다 클 경우
if(position_min<temp_vertical.position[0])
{
temp_vertical.position[0] = position_min;
}
temp_vertical.position[1] = position_max;
removal.add(current.clone());
}
//temp_vertical의 min이 current의 min, max사이에 있을경우
else if(position_min<= temp_vertical.position[0] && temp_vertical.position[0] <=position_max)
{
//temp_vertical의 max가 current의 max보다 작을 경우
/*
if(temp_vertical.position[1]<position_max)
{
temp_vertical.position[1] = position_max;
}
*/
temp_vertical.position[0] = position_min;
removal.add(current.clone());
}
//temp_vertical의 max,min사이에 current의 min, max이 위치할 경우
else if(temp_vertical.position[0] < position_min && position_max < temp_vertical.position[1])
{
removal.add(current.clone());
//removal.add(current);
}
}
//만약 위의 if,else if문의 실행결과 temp_vertical.position과 current의 값이
//같아진다면, map.get(i).add(temp_vertical);를 실행해도 중복처리 되기 때문에
//추가가 안된다. 따라서, map.get(i).removeAll(removal);를 먼저 실행해야 한다.
map.get(i).removeAll(removal);
map.get(i).add(temp_vertical);
}
}
}
// map.keySet() => map.keySet()의 자료형은 Set<Integer>
/*
Set_x
[0,3,4,5]
[1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9]
[1,2,3,4]
Set_y
[1,3,4]
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
[2,4,5,7]
map
{
"0":[{"position":[1,5]}],
"1":[{"position":[0,7]}],
"2":[{"position":[1,7]}],
"3":[{"position":[1,6]}],
"4":[{"position":[3,6]}],
"5":[{"position":[3,7]}],
"6":[{"position":[5,7]}]
}
*/
long height;
long sum=0;
//HashMap<Integer, HashSet<vertical_length>> map = new HashMap<Integer, HashSet<vertical_length>>();
for(Integer key : map.keySet())
{
height = 0;
for(vertical_length pos : map.get(key))
{
//map.get(key).pos.leng += Set_y.get(pos.position[1])-Set_y.get(pos.position[0]);
height += Set_y.get(pos.position[1])-Set_y.get(pos.position[0]);
}
sum += height * Long.valueOf(Set_x.get(key+1) - Set_x.get(key));
}
return sum;
}
class vertical_length implements Cloneable
{
int[] position = new int[2];
//서로 다른 배열이, 같은 성분들로 구성되어 있을경우 비교하기위한 코딩
//hashCode는 각 객체의 주소값을 반환하여 생성한 객체의 고유 정수값.
//hashCode 오버라이딩,주소값이 다르나, 구성 요소들이 동일한 객체에 hashCode를
//같게 오버라이딩 해줌으로써,equals가 제대로 수행가능하게 해준다.
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
//Objects,hash(Object... values) 메서드 => 매개 값으로 주어진 값들을 이용해서 해시 코드를 생성한다.
//hashcode => 객체를 식별하기위한 정수값
//return Objects.hash(position);
return Objects.hash(this.position[0],this.position[1]);
}
//equals 오버라이딩
//hash 값을 사용하는 Collection(HashMap, HashSet, HashTable)등에서
//.add()메소드등을 실행할 경우가 있다. 기존 구성요소와 추가되는 객체의 중복여부를
//확인하기 위해 아래와 같은 과정을 거처야 한다.
//1)비교하는 두 객체의 hashCode()메소드 리턴값이 같아야 한다
// (Object 클래스의 hashCode 메소드는 객체의 고유한 주소 값을
// int 값으로 변환하기 때문에 객체마다 다른 값을 리턴)
//2)equals 메서드의 리턴 값이 true여야 논리적으로 같은 객체라고 판단
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
//equals의 인자로 받은 obj가 vertical_length의 인스턴스인지 확인한다.
if(obj instanceof vertical_length)
{
//Object 타입의 자료형을, vertical_length로 다운캐스팅 한다.
vertical_length comp = (vertical_length)obj;
//array1.equals(array2), array1 == array2 => 두 배열이 같은 객체인지를 비교한다.
//Arrays.equals(array1,array2) => 두 배열의 내용물들이 같은지를 비교한다.
return Arrays.equals(this.position, comp.position);
//return this.position[0] == comp.position[0] && this.position[1] == comp.position[1];
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
@Override
/*
vertical_length는 내가 정의한 클래스로, Object 클래스와 상속관계가
없기 때문에 오버라이딩 없이 clone()메소드 사용할 수 없다.
=> vertical_length의 객체에 대해 깊은복사 기능을 사용하기 위해서
clone() 메소드를 오버라이딩하고,접근 제어자를 Public으로 바꾼다.
(참고 : Object.java에서 아래와 같이 clone()이 정의되어 있다.
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;)
https://velog.io/@roro/Java-Object-%ED%81%B4%EB%9E%98%EC%8A%A4-clone
*/
public vertical_length clone()
{
Object obj = null;
try
{
//super는 자식 클래스가 부모 클래스로부터 상속받은 멤버를 참조할 때 사용하는 참조 변수
obj = super.clone();
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException e)
{
}
return (vertical_length)obj;
}
}
}
실행결과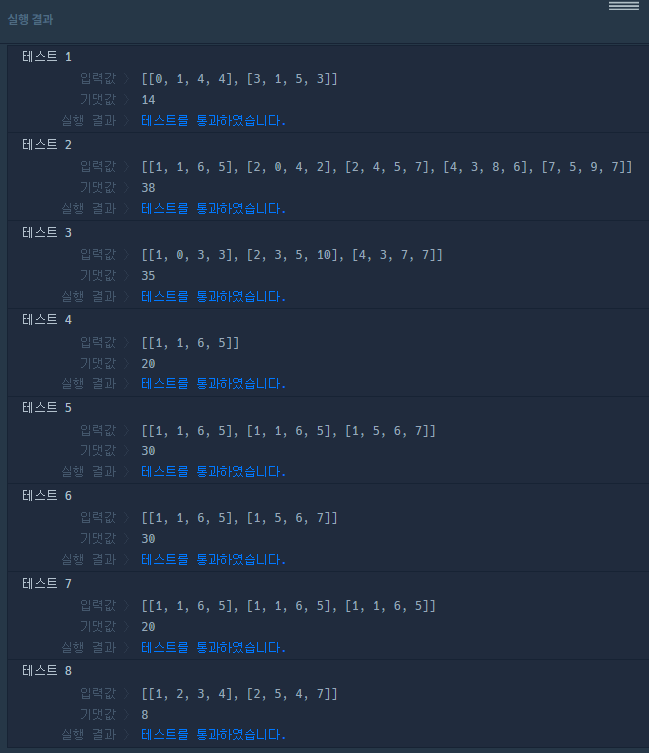
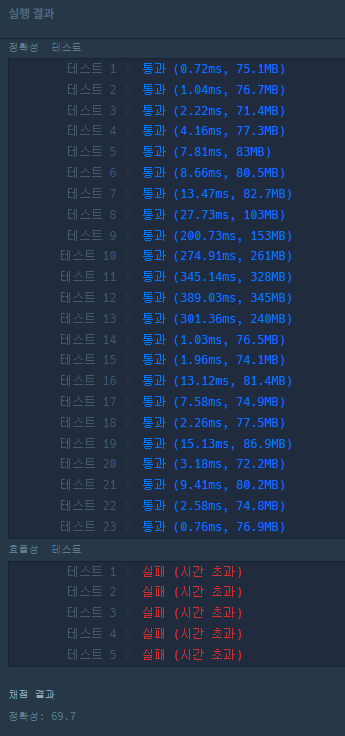 테스트케이스8개와 정확성 테스트는 통과했지만, 효율성 테스트는 그렇지 못했다. 추측하건데, 직사각형이 겹쳤을때, 길이를 구하는 과정에서 많은 시간이 걸리는것 같다.
테스트케이스8개와 정확성 테스트는 통과했지만, 효율성 테스트는 그렇지 못했다. 추측하건데, 직사각형이 겹쳤을때, 길이를 구하는 과정에서 많은 시간이 걸리는것 같다.
댓글남기기