직사각형의 넓이2(프로그래머스 Lv5)
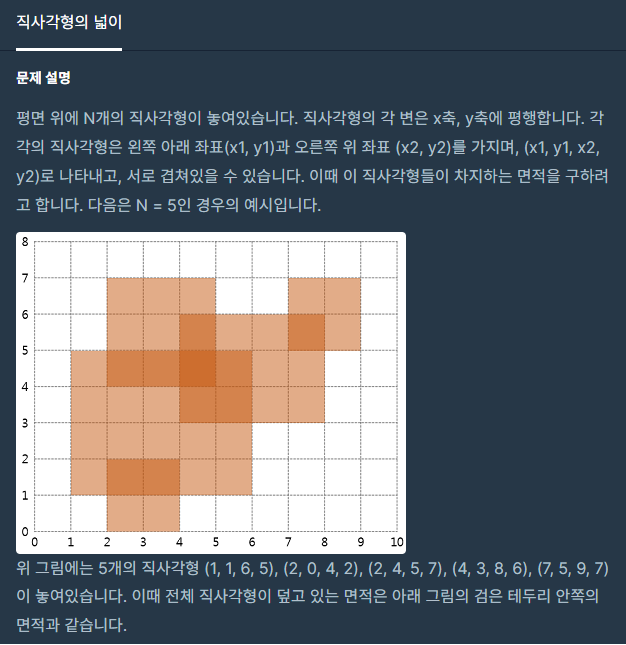
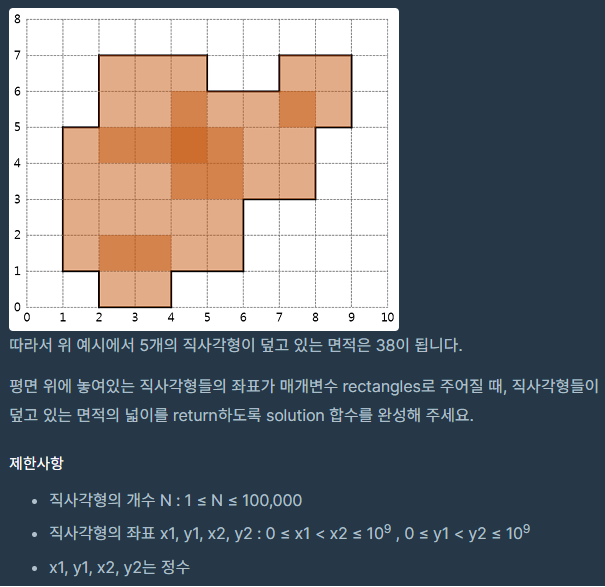
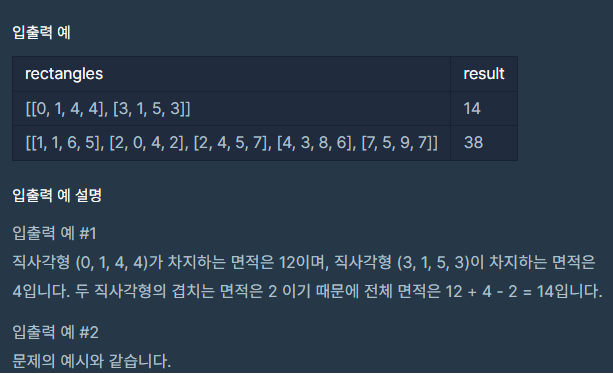
코드의 작동원리 설명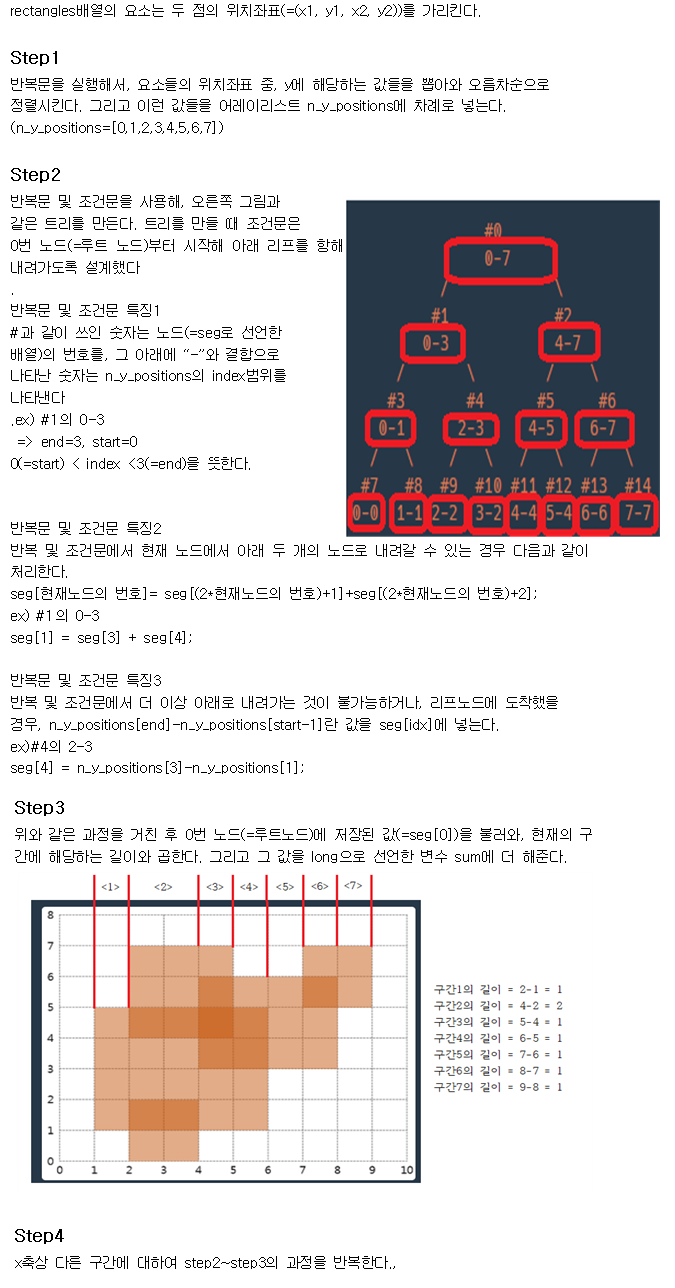
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
public long solution(int[][] rectangles)
{
TreeSet<Integer> y_positions = new TreeSet<Integer>();
ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<int[]>();
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int[] rec : rectangles)
{
y_positions.add(rec[1]);
y_positions.add(rec[3]);
list.add(new int[]{rec[0],rec[1],rec[3],1});
list.add(new int[]{rec[2],rec[1],rec[3],-1});
}
//for문 실행결과
/*
y_positions
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
list
[
[1,1,5,1],
[6,1,5,-1],
[2,0,2,1],
[4,0,2,-1],
[2,4,7,1],
[5,4,7,-1],
[4,3,6,1],
[8,3,6,-1],
[7,5,7,1],
[9,5,7,-1]
]
*/
//list를 정렬하기 위한 코드
/*
Comparator<int[]> comparator = new Comparator<int[]>()
{
@Override
public int compare(int[] first, int[] second)
{
//0번째 인덱스가 가리키는 값이 작은 순(오름차순)으로 정렬한다.
//(반드시 -1, 1일 필요는 없다, 걍 음수 양수 구분만 하기 위한 용도일 뿐이다.
//음수일 때 요소 앞뒤 위치를 바꿔준다)
return (first[0] - second[0] > 0) ? 1 : -1;
//조건이 같은거 같은데 아래와 같이 리턴하면, 런타임시 에러가 발생하는 경우가 있다.
(이유는 모르겠다.)
//return (first[0] - second[0] < 0) ? -1 : 1;
//compare작업시, list맨 끝에값을 first, 그 앞의 값을 second에 넣고 작업하고,
//이후 한칸씩 앞으로 움직이며, first, second에 집어넣는거 같다.
}
};
Collections.sort(list, comparator);
*/
//위의 comparator관련 코드 작성하지 않고 아래와 람다식을 사용해서 한줄로도 오름차순 가능하다.
Collections.sort(list, (first, second) -> first[0] - second[0]);
/*
list정렬
[
[1,1,5,1],
[2,4,7,1],
[2,0,2,1],
[4,3,6,1],
[4,0,2,-1],
[5,4,7,-1],
[6,1,5,-1],
[7,5,7,1],
[8,3,6,-1],
[9,5,7,-1]
]
*/
//데이터타입이 트리셋인 y_positions를 어레이리스트로 변환한다.
ArrayList<Integer> n_y_positions = new ArrayList<Integer>(y_positions);
//n_y_positions=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
/*세그먼트 트리의 맨 아래층이 한곳이라도 비지않게 표현하려면, 아래와 같이 루트노드의 숫자가 나타내는
n_y_positions의 index범위의 크기가 2,4,8,...2^n개의 형태가 되어야한다.
#0
0-1
/ \ => 새그먼트 트리의 크기 = (2^2) -1 = 3
#1 #2
0-0 1-1
#0
0-3
/ \
#1 #2
0-1 2-3 => 새그먼트 트리의 크기 = (2^3) -1 = 7
/ \ / \
#3 #4 #5 #6
0-0 1-1 2-2 3-3
...
*/
int vol=2;
for(int i=0; i<n_y_positions.size(); i++)
{
map.put(n_y_positions.get(i), i);
if(!(vol/2 <= n_y_positions.size()-1 && n_y_positions.size()-1 < vol))
{
vol *=2;
}
}
//배열 선언시, 따로 값을 넣어주지 않으면 0으로 초기화가 된다.
//seg의 크기는 vol의 2배에서 하나가 적게 설정한다.
//(그래야 세그먼트트리 온전히 구성 가능하다.)
//주의!!
//int[] seg로 선언할 경우, 계산해야할 직사각형의 넓이가 크다면
//int범위를 벗어난 숫자가 seg의 원소로 들어갈 수 있기 때문에
//오류 발생 가능성이 있다.
long[] seg = new long[2*vol-1];
int[] spanning = new int[2*vol-1];
int[] temp;
int start;
int end;
int renewed_start;
int renewed_end;
int idx;
int prev_x = list.get(0)[0];
int cur_x;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();
Stack<int[]> stack = new Stack<int[]>();
long sum=0;
for(int j=0; j<list.size(); j++)
{
cur_x = list.get(j)[0];
sum += (cur_x - prev_x) * seg[0];
/*아래와 같이 코딩시,n_y_positions에서 list.get(j)[1]의 인덱스를
찾는것에 시간이 많이 소모된다.(효율성 테스트 탈락의 원인)
start = n_y_positions.indexOf(list.get(j)[1])+1;
*/
start=map.get(list.get(j)[1])+1;
end = map.get(list.get(j)[2]);
queue.add(new int[]{0,0,vol-1});
while(queue.size() !=0)
{
temp = queue.poll();
idx = temp[0];
renewed_start = temp[1];
renewed_end = temp[2];
//renewed_start,renewed_end와 start,end의 범위가 겹치지 않는 경우
if(renewed_end < start || end < renewed_start)
{}
//start,end의 범위안에 renewed_start,renewed_end가 있는 경우
else if(start<=renewed_start && renewed_end<=end)
{
spanning[idx] += list.get(j)[3];
stack.push(new int[]{idx,renewed_start,renewed_end});
}
//renewed_start,renewed_end와 start,end의 범위가 일부 겹치는 경우
else
{
if(idx < vol-1)
{
queue.add(new int[]{2*idx+1,renewed_start,(renewed_start+renewed_end)/2});
queue.add(new int[]{2*idx+2,(renewed_start+renewed_end)/2+1,renewed_end});
}
stack.push(new int[]{idx,renewed_start,renewed_end});
}
}
while(!stack.empty())
{
temp = stack.pop();
idx = temp[0];
renewed_start = temp[1];
renewed_end = temp[2];
//n_y_positions의 인덱스 temp[1]와 temp[2]에 걸친 공간이 점유되었는지 판단한다.
if(spanning[idx] != 0)
{
seg[idx] = n_y_positions.get(renewed_end) - n_y_positions.get(renewed_start-1);
}
//n_y_positions의 인덱스 temp[1]와 temp[2]에 걸친 공간이 점유되어있지 않다.
//&& idx가 vol-1보다 작으면 seg[idx]의 값을 자식 노드의 합으로 구성한다.
else if(idx < vol-1)
{
seg[idx] = seg[2*idx+1] + seg[2*idx+2];
}
//n_y_positions의 인덱스 temp[1]와 temp[2]에 걸친 공간이 점유되어있지 않다.
//&& idx가 vol-1이상이다.
else
{
seg[idx] = 0;
}
}
prev_x = cur_x;
}
return sum;
}
}
실행결과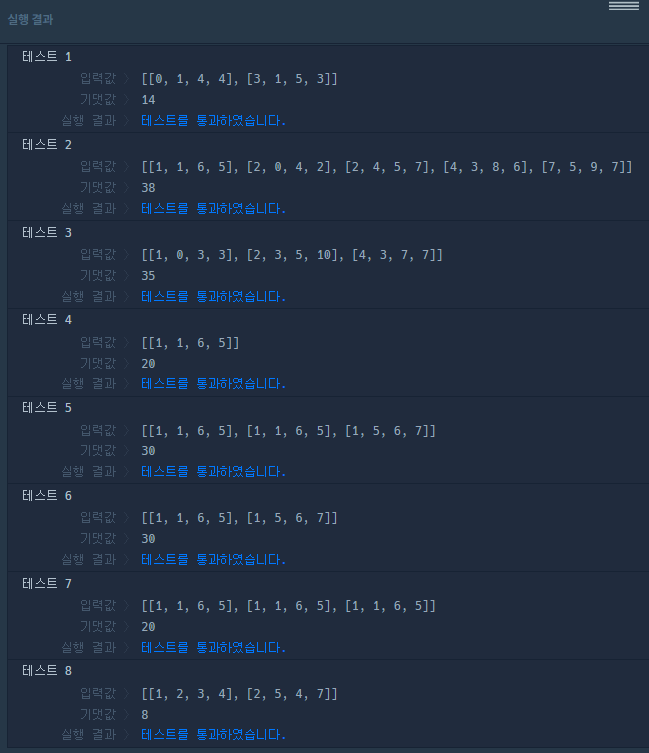
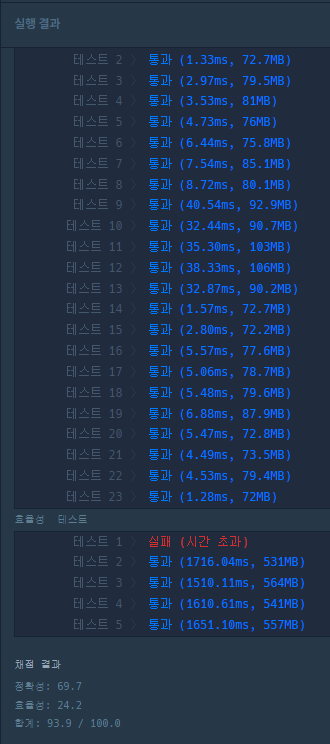 저번과 다르게 효율성 테스트에서 하나만 빼고 다 성공했다. Queu와 Stack에 값을 넣고 빼는 과정에서 많은 시간이 소요된것이 시간초과의 원인이 된것같다.
저번과 다르게 효율성 테스트에서 하나만 빼고 다 성공했다. Queu와 Stack에 값을 넣고 빼는 과정에서 많은 시간이 소요된것이 시간초과의 원인이 된것같다.
댓글남기기