직사각형의 넓이3(프로그래머스 Lv5)
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
int vol=2;
long[] seg;
int[] spanning;
ArrayList<Integer> n_y_positions = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public long solution(int[][] rectangles)
{
TreeSet<Integer> y_positions = new TreeSet<Integer>();
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for(int[] rec : rectangles)
{
y_positions.add(rec[1]);
y_positions.add(rec[3]);
list.add(new int[]{rec[0],rec[1],rec[3],1});
list.add(new int[]{rec[2],rec[1],rec[3],-1});
}
/* for문 실행결과
y_positions
[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
list
[
[1,1,5,1],
[6,1,5,-1],
[2,0,2,1],
[4,0,2,-1],
[2,4,7,1],
[5,4,7,-1],
[4,3,6,1],
[8,3,6,-1],
[7,5,7,1],
[9,5,7,-1]
]
*/
//list를 정렬하기 위한 코드
/*
Comparator<int[]> comparator = new Comparator<int[]>()
{
@Override
public int compare(int[] first, int[] second)
{
//0번째 인덱스가 가리키는 값이 작은 순(오름차순)으로 정렬한다.
//(반드시 -1, 1일 필요는 없다, 걍 음수 양수 구분만 하기 위한 용도일 뿐이다.
//음수일 때 요소 앞뒤 위치를 바꿔준다)
return (first[0] - second[0] > 0) ? 1 : -1;
//조건이 같은거 같은데 아래와 같이 리턴하면, 런타임시 에러가 발생하는 경우가 있다.
(이유는 모르겠다.)
//return (first[0] - second[0] < 0) ? -1 : 1;
//compare작업시, list맨 끝에값을 first, 그 앞의 값을 second에 넣고 작업하고,
//이후 한칸씩 앞으로 움직이며, first, second에 집어넣는거 같다.
}
};
Collections.sort(list, comparator);
*/
Collections.sort(list, (first, second) -> first[0] - second[0]);
//데이터타입이 트리셋인 y_positions를 어레이리스트로 변환한다.
n_y_positions = new ArrayList<Integer>(y_positions);
/*세그먼트 트리의 맨 아래층이 한곳이라도 비지않게 표현하려면,
아래와 같이 루트노드의 숫자가 나타내는 n_y_positions의 index범위의
크기가 2,4,8,...2^n개의 형태가 되어야한다.
#0
0-1
/ \ => 새그먼트 트리의 크기 = (2^2) -1 = 3
#1 #2
0-0 1-1
#0
0-3
/ \
#1 #2
0-1 2-3 => 새그먼트 트리의 크기 = (2^3) -1 = 7
/ \ / \
#3 #4 #5 #6
0-0 1-1 2-2 3-3
...
*/
for(int i=0; i<y_positions.size(); i++)
{
map.put(n_y_positions.get(i), i);
if(!(vol/2 <= n_y_positions.size()-1 && n_y_positions.size()-1 < vol))
{
vol *=2;
}
}
//배열 선언시, 따로 값을 넣어주지 않으면 0으로 초기화가 된다.
//seg의 크기는 vol의 2배에서 하나가 적게 설정한다.
//(그래야 세그먼트트리 온전히 구성 가능하다.)
//주의!!
//int[] seg로 선언할 경우, 계산해야할 직사각형의 넓이가 크다면
//int범위를 벗어난 숫자가 seg의 원소로 들어갈 수 있기 때문에
//오류 발생 가능성이 있다.
seg = new long[2*vol-1];
spanning = new int[2*vol-1];
int prev_x = 0;
long sum=0;
for(int j=0; j<list.size(); j++)
{
sum += (list.get(j)[0] - prev_x) * seg[0];
/*
아래와 같이 코딩시,n_y_positions에서 list.get(j)[1]의 인덱스를
찾는것에 시간이 많이 소모된다.(효율성 테스트 탈락의 원인)
n_y_positions.indexOf(list.get(j)[1])+1;
*/
renewal(0,0,vol-1,map.get(list.get(j)[1])+1,map.get(list.get(j)[2]),list.get(j)[3]);
prev_x = list.get(j)[0];
}
return sum;
}
void renewal(int idx, int renewed_start, int renewed_end, int start, int end, int incre)
{
//renewed_start,renewed_end와 start,end의 범위가 겹치지 않는 경우
if(renewed_end < start || end < renewed_start)
{
return;
}
//start,end의 범위안에 renewed_start,renewed_end가 있는 경우
else if(start<=renewed_start && renewed_end<=end)
{
spanning[idx] += incre;
}
//renewed_start,renewed_end와 start,end의 범위가 일부 겹치는 경우
else
{
int center = (renewed_start+renewed_end)/2;
renewal(2*idx+1,renewed_start,center, start, end, incre);
renewal(2*idx+2,center+1,renewed_end, start, end, incre);
}
//n_y_positions의 인덱스 temp[1]와 temp[2]에 걸친 공간이 점유되었는지 판단한다.
if(spanning[idx] != 0)
{
seg[idx] = n_y_positions.get(renewed_end) - n_y_positions.get(renewed_start-1);
}
//n_y_positions의 인덱스 temp[1]와 temp[2]에 걸친 공간이 점유되어있지 않다.
//&& idx가 vol-1보다 작으면 seg[idx]의 값을 자식 노드의 합으로 구성한다.
else if(idx >= vol-1)
{
seg[idx] = 0;
}
//n_y_positions의 인덱스 temp[1]와 temp[2]에 걸친 공간이 점유되어있지 않다.
//&& idx가 vol-1이상이다.
else
{
seg[idx] = seg[2*idx+1] + seg[2*idx+2];
}
}
}
실행결과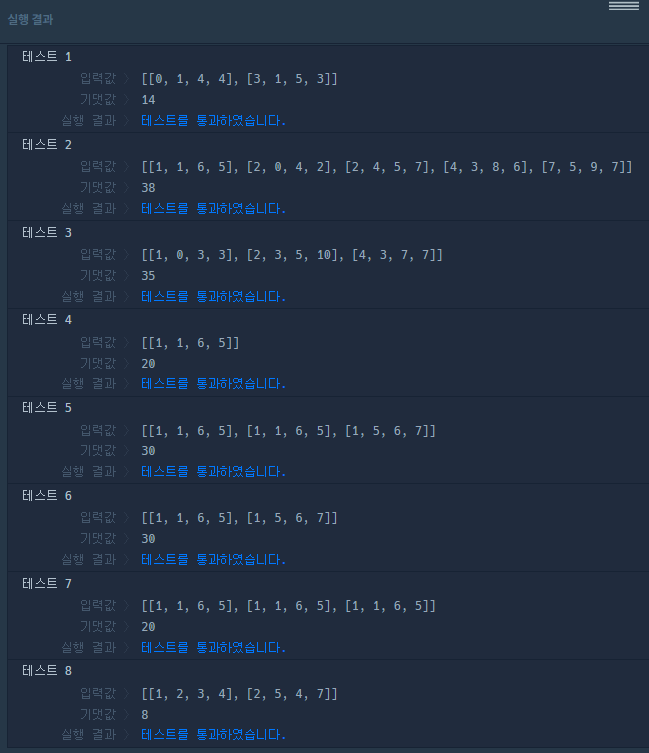
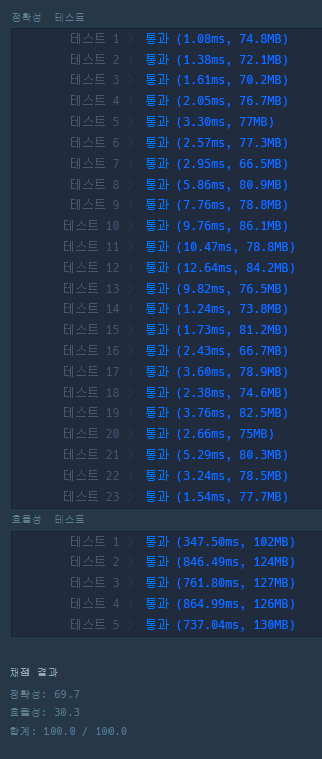 직사각형의 넓이2와 전체적인 동작원리는 동일하다. 하지만, Queue와 Stack을 사용하는 대신 재귀호출을 하는 방법을 이용해 시간초과 문제를 완전히 해결하였다.
직사각형의 넓이2와 전체적인 동작원리는 동일하다. 하지만, Queue와 Stack을 사용하는 대신 재귀호출을 하는 방법을 이용해 시간초과 문제를 완전히 해결하였다.
댓글남기기